Animal Cell Definition Biography
Source:- Google.com.pk
Cell
Definition
noun
(Science: Cell Biology)
1. The structural, functional and biological unit of all organisms.
2. An autonomous self-replicating unit that may exist as functional independent unit of life (as in the case of unicellular organism), or as sub-unit in a multicellular organism (such as in plants and animals) that is specialized into carrying out particular functions towards the cause of the organism as a whole.
3. A membrane bound structure containing biomolecules, such as nucleic acids, proteins, and polysaccharides.
Supplement
There are two distinct types of cells: prokaryotic cells (e.g. bacterial cells) and eukaryotic cells (e.g. plant or animal cell). The main difference between the two is a well-defined nucleus surrounded by a membranous nuclear envelope present only in eukaryotic cells. Despite this difference they share a number of common features: the genetic information is stored in genes, proteins serve as their main structural material, ribosomes are used to synthesize proteins, adenosine triphosphate is the main source of metabolic energy to sustain various cellular processes, and a cell membrane that controls the flow of substances into and out of the cell.
Word origin: From Latin cella.
Related forms: cellular (adjective)
See also: cell biology, cytology, stem cell.
terms
What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. 1) reproduction: amoeba dividing into two. 2) growth and development: sand dollar embryo dividing after fertilization. 3) tissue renewal: Bone marrow cells divide and give rise to new bone marrow.
What is mean by the cell cycle? Life of a cell from the time it is formed, from a dividing parent cell, to its division into 2 cells.
What is the meaning of genome? All of a cell's genetic information.
What is the difference between a humans genome to that of a prokaryotic cell? Human genome is made up of many molecules of DNA, not just one circular molecule.
How many chromosomes are in a human somatic cell? 46
Name two types of somatic cells in your body. Liver cells, skin cells.
What is a gamete? Reproductive cell.
Name the two types of gametes. Sperm, egg.
How many chromosomes in a human genome? 46.
Define chromatin. Complex of DNA and protein molecules.
Define chromosome. Packaged DNA molecule.
Define chromatid. 1 of 2 identical chromosomal strands.
Define centromere. Specialized region where 2 chromatids are close together
Define mitosis. Division of the nucleus
Define cytokinesis. Division of the cytoplasm.
What are the components of the mitotic spindle? Fibers made of microtubules and associated proteins.
What is the source of the components that make up the mitotic spindle? Microtubules from the cytoskeleton.
What is another name for the centrosome? Microtubule organizing center
What happens to the centrosome during interphase? Prophase? In interphase they replicate, in prophase they move to polar ends.
What is a kinetochore? A structure o fproteins associated with specific sections of chromosomal DNA at the centromere.
What is the difference between kinetochore and nonkinetechore microtubules. Kinetochore microtubules attach to the kinetochore of chromosomes and the real the chromosomes in during anaphase. Nonkinetechore microtubules do not attach to chromosomes but they do work to elongate the cell.
What are the components of the mitotic spindle? Centrisomes and microtubules.
At what end do kinetichore microtubules shorten during anaphase? From the kinetichore side.
Describe cytokinesis in an animal cell. Contractile ring of actin cleaves the cytoplasm.
Describe cytokinesis in a plant cell. Vesicles form a cell plate that divides daughter cells.
How is the cell plate formed? Vesicles from the golgi move along the cytoskeleton and coalesce to form the cell plate.
Describe binary fusion. As chromosomal replication begins, the origin of replication produces 2 origins. They travel to opposite sides as chromosomes and replicate. Plasma membrane then grow inwards.
What are the differences in how prokaryotic cells vs. eukaryotic cells reproduce? Prokaryotes partake in binary fusion, eukaryotes use mitosis and meiosis.
What are the difference in how prokaryotic cells vs. eukaryotic cells in their number of chromosomes. Prokaryotes have 1 long circular strand, eukaryotes have many molecules of DNA. ...
What are the difference in how prokaryotic cells vs. eukaryotic cell shave the shape of chromosomes. In prokaryotes they are circular, in eukaryotes, they come in pairs. ...
What control the cell cycle? Various mechanisms, one being molecules present in the cytoplasm.
What is a cell cycle check point? Cell cycle control point where stop and go signals regulate the cycle.
What happens at G1 check point and how is it controlled? Protein kinases give the go ahead for continued growth of organelles.
What happens at G2 check point and how is it controlled? Cdc gives the go ahead for continued growth.
What happens at M check point and how is it controlled? MPF controls this check point. If cells pass this check point, they continue on to cell division.
What is the G0 phase? If the cell does not receive the go ahead for G1, it goes to G0 where it does not replicate.
What is a protein kinase? Proteins that activate / inactivate other proteins by phosphorilation.
Kinase drives the cell cycle, but they must be activated by attachment of a _______. Cyclin.
The activity of cyclin-dependent kinases rises and falls. Why? Because its cyclin partner concentration varies.
What does MPF trigger? "M phase"
Animal Cell Definition Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Definition Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Definition Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Definition Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Definition Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake

Animal Cell Definition Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Definition Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake

Animal Cell Definition Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake
Animal Cell Definition Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake


Animal Cell Definition Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake
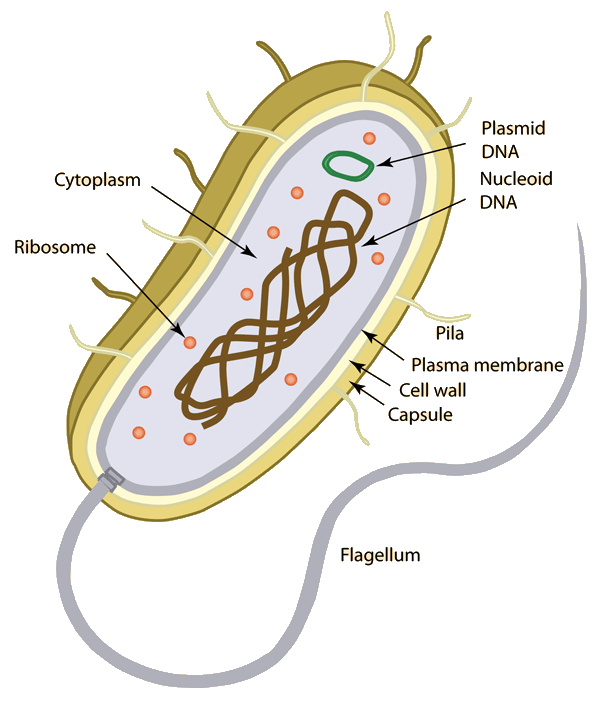

Animal Cell Definition Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake
No comments:
Post a Comment